If batteries are your passion you may have noticed some stories popping up recently about an all new portable energy storage product that some are claiming will make batteries a thing of the past. Articles have been circulating that there is a new technology in town with mind blowing potential. The product is the super-capacitor.
Here are just a few characteristics that have super-capacitors turning heads:
- They can charge to full capacity within seconds.
- They can be made so thin they could form part of your clothing but are 100 times stronger than steel.
- They will charge and discharge an unlimited amount of times.
- They’re much lighter than Lithium Ion (the battery type that powers phones and laptops) or to be more accurate they hold up to 10 times more power per kilogram.
- Its possible to 3D print or screen print them.
But before you start reaching for the champagne because you think the grindingly slow process of charging batteries is over and your coat can double as a spare power source for tomorrow … hold up, its not all positive.
- They will almost completely self-discharge within a couple of months – compared to sealed lead acid batteries or lithium ion batteries which only self-discharge by a few percentage points over the same period.
- They can’t offer constant voltage or capacity during discharge
- They’re very expensive to produce (at the moment)
Lets take a closer look.
What exactly is a super-capacitor?
A super-capacitor is a completely different beast compared to a battery when it comes to energy storage, so although many people refer to super-capacitors as batteries they are actually nothing of the sort in the technical sense.
Batteries are made up of many materials and store power in a chemical form. Connecting them to a circuit causes a chemical reaction but one that can only take place at a certain speed. Try to charge or discharge too fast and the battery resists, building up heat and creating a potential for explosions and fires.
These chemical reactions cause wear on the internal parts and this is why batteries only have a limited time span, they can only charge and recharge a certain number of times before they die.
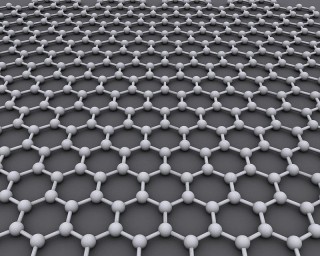
A super-capacitor on the other hand is based on graphene, a type of carbon. At an atomic level graphene is two dimensional (most material molecules are three dimensional) which gives it an ultra thin quality.
Electricity can be stored on its surface. With no chemical reactions taking place it can charge and discharge in seconds and materials suffer minimal wear and tear in the process.
The principle of energy storage is exactly the same effect that you experience when taking off a sweater and then feeling a shock as you a touch an earthed item such as a faucet. You took on the charge in an instant and discharged in a fraction of a second.
Graphene is also highly porous which means the surface area available to store power is optimized even though it is 2D. Not only can it take on power fast, a small amount can take a great deal of it.
The future of portable power?
While super-capacitors have some awe inspiring characteristics and are already replacing batteries in some areas, they are not perfect for every application. See our article Superconductors versus Batteries for a detailed comparison.


What is the price of super capacitor? I want 12 volt DC power to store for long time